By Ján Lunter, Founder and CEO at Innovatrics
The metaverse is on everyone’s minds, and most of us are mesmerized by the idea of spending parts of our time in a parallel, virtual reality. Soon, people and businesses will interact with each other, share information, test products together, and perform service agreements completely online, present in a 3D world.
However, there are two sides to every coin. With cyber threats, fraud, and identity theft already disrupting the existing, much less immersive digital reality, we need to ask: How can we ensure that the person or company we interact with virtually is who we think they are? What if somebody else embodies my character online? Can we protect our 3D gadgets and our data from identity theft?

Still, companies don’t have to jettison their future B2B meta-reality. By looking at what opportunities and risks the metaverse presents, we learn how thorough, reliable, and convenient identity verification can help protect your identity and the identities of others in the metaverse.
What the B2B Metaverse Will Look Like
If we want to foresee the role of B2B in this virtual world, we can compare it to the current state of B2B on social networks. Digital interactions enable smoother relationships between businesses on a global scale, and that’s what the metaverse will soon be able to do even better.
For example, the metaverse will potentially change hiring and onboarding practices. There will be an opportunity to organize an interview in a virtual 3D office and approach the future work area “together” (for example, by showing the product digitally or previewing a typical working day). This will help find a better candidate fit for a role and allow applicants to get to know the working environment in a close-up.
The metaverse will also be effective for finding new business partners as virtual reality conferences can be more immersive – without being expensive or requiring travel. And it will significantly improve marketing strategies if you offer virtual showrooms and 3D product reviews to potential customers. Overall, the metaverse can make B2B interactions more efficient and lower the barriers to entry, which leads to new markets opening up.
Security Threats for B2B Interactions in the Metaverse
The problem with the internet is that people share, contribute, and store a lot of personal information and sensitive data there. In 2020, identity theft increased by 42% compared to 2019 due to rapid digitization. Events like the LinkedIn breach that exposed 700 million user records have shaken the digitized world to the bone. The most significant security risk for business activities is the one we see nowadays on social networks. You can never be 100% sure that you interact with the exact person you want to connect with – or with a real person altogether.
In the metaverse, where people will enter more networks via various tools (goggles, devices, computers, and various platforms), the risk of fraud or device theft is much higher, and catching the perpetrator remains challenging. The more data of us is stored online, the better it must be secured against fraud. Since the metaverse is more immersive, the main focus should be on verifying and preserving the identity of the user.
Technologies Guaranteeing Meta-Security
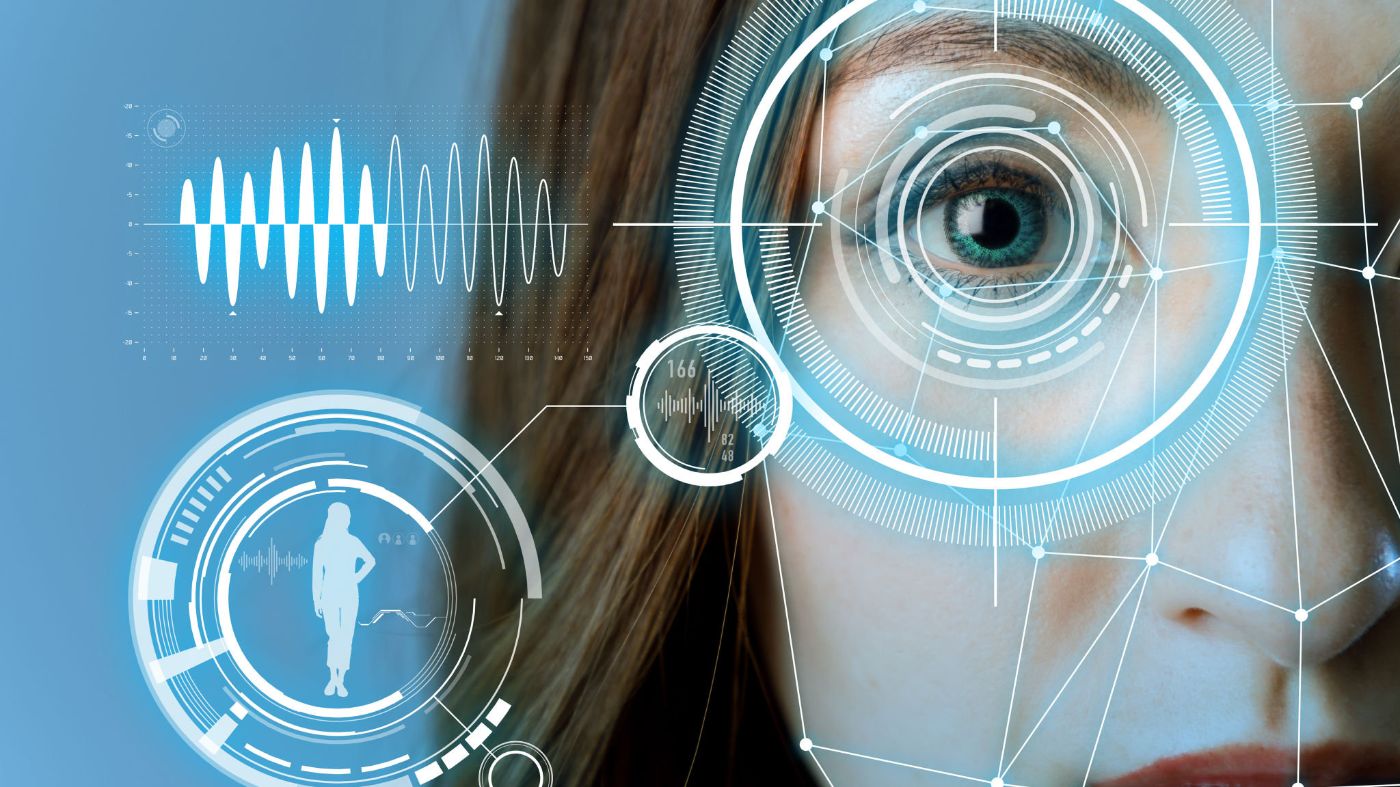
B2B businesses need to implement good verification infrastructures to counterfeit identity theft. To enter the metaverse, we will most likely use 3D technology equipped with headsets and VR glasses. Out of the various methods available to accessing such gadgets safely – like software tokens or passwords – biometric identification technology is one method.
Biometrics uses the individual characteristics of a registered person, such as fingerprints or iris scans, to establish the true identity of a login attempt and give a user access to their account. Even though biometric technology is already an essential part of the current security ecosystem, with a market size of $30 billion, it can work even better with 3D technology for entering virtual reality.
As biometrics are platform-agnostic, you can leverage biometric verification for customer verification processes on phones, desktops, augmented reality glasses, or browsers. And even if a computer doesn’t have a camera, users can take their smartphone, perform facial recognition, and transmit the green light to the PC via a QR code. This makes biometrics very convenient when used for various gadgets. Compared with tokens and passwords, biometric authentication is faster and more seamless. Users have their biometric data (such as their iris) at hand all the time, and it can’t be forgotten or lost.
How to Use Biometrics to Access Digital Worlds
With a 99% success rate, iris scans are currently the most reliable biometric modality. Periodic checks will ensure that the user of the VR goggles has not switched for another person. The system can have additional alert mechanisms, for example, through geolocation data. If the goggles move out of the usual space, this could require additional verification. The idea is to validate a person’s authorized access by a combination of biometrics and other authentication elements (e.g. a second software device as seen with Google’s 2-step verification).
To minimize the risk of fraud, the social network operator (which might be the company itself) in the metaverse shouldn’t have complete control over the biometric identity information and user data. The chosen identity authentication system could, for example, work with blockchain technology to help people stay in control of their personal data and how they are used – something already being pursued by EU countries. The blockchain would keep personal data under a user’s control because it cannot be changed once it’s on the public ledger. The service would just check against the blockchain whether the data user is genuine and transmit the information via a QR code. This so-called self-sovereign identity attempts to solve the problem of providing personal info to service providers without risking data misusage.
If the metaverse obtains the proof of identity of a user, it could pass it directly to third parties (just like the login with Google Sign-in buttons). Having one central control of a customers’ identity instead of storing the data in apps like Twitter and Google will make access to your company’s B2B metaverse fast and seamless.
Once we fully enter the metaverse, identity security will be a crucial issue. The key to a fully immersive metaverse without risk is not to rely on a particular provider who could fall victim to identity theft. Only if identity fraud is mitigated can we enjoy the metaverse’s perks for B2B relationships.
This article was originally published by Ján Lunter at: How biometrics can prevent identity theft in the metaverse.
For more market insights, check out our latest Digital Twin news here.