Extended reality merges the physical and virtual worlds using various algorithms and hardware devices such as cameras and sensors. With over 57.4 million VR users worldwide, extended reality technology is becoming more and more mainstream. Tech giants like Apple have contributed immensely towards AR adoption by equipping all the latest phones and gear with AR capabilities.
Therefore, this article provides an extensive overview of extended reality, its technology, how we use it in our daily lives, and the future of extended reality. We’re nearing the end of 2022 and have come far from the first VR technology, a Sensorama Machine, created in 1956. So, keep reading to learn about this technology and all the recent developments.
What is Extended Reality?
You might have either already played the game Pokémon Go or at least have heard about it from one of your friends. This game features augmented reality mode (a part of extended reality), where different Pokémon characters are brought to your physical world environment. It could be directly in front of you, or you might see directions on Google maps that locate the position of your Pokémon character. Individuals would have to move their cameras around to find the Pokémon, making it a very interactive experience.

But how can you watch animated Pokémon characters in your physical world? What is the technology behind it? Extended Reality (XR) technology is an umbrella term that encompasses VR, AR, and MR technologies.
You can take Metaverse as an upcoming, ongoing, and rapidly developing sector of technology under the umbrella of Extended Reality and augmented reality (AR), mixed reality (MR), and virtual reality (VR). Companies such as Meta are working on creating immersive technologies to enable users to step into entirely virtual realms to work, interact, play and shop.
See also: What is Metaverse? Guide into the Future of Digital Reality
Common Devices and Applications of Extended Reality
As mentioned previously, Extended Reality consists of numerous image-processing algorithms, sensors, cameras, and much more. In addition, users can put on wearable devices such as headsets, haptic feedback gloves, complete bodysuits, and much more.
A simple example of Extended Reality today is the famous application Snapchat. Many use Snapchat filters to take pictures and enhance them with different virtual elements. For example, you can add ears, pirate patches, beards, and more as virtual elements. You can even tweak eye colors, high-pitched voices, and much more!
So, if you are currently using Snapchat with these filters, then you are already utilizing Augmented Reality in your day-to-day life. All these filters, virtual accessories, ear shapes, eye colors, and others are part of AR. Similarly, users can play many games through virtual reality, such as Minecraft and Beat Saber. Many individuals have been able to experience VR through these games.
However, the most exclusive form of Extended Reality is Mixed Reality. This type of XR is not widely accessible because it is costly. The Microsoft Hololens 2 headset costs around $3500, which is very expensive compared to Meta’s VR headset at $399.
MR takes the AR experience further by superimposing virtual elements onto the physical realm that users can touch, move around, and interact with. The technology uses a “hologram” based approach and offers the most immersion compared to VR and AR. MR is currently being used in industrial metaverses by large organizations such as Heinz and Kawasaki.
So, when exactly did Extended Reality come into existence? Keep on reading to find out.
Start of Extended Reality and Its Evolution
Many believe that the first VR technology was introduced in 1956; that was the start of Extended Reality. However, the concept of Extended Reality started in the early 1800s. We’ve provided a summary of the existence of XR below.
During the 1800s
The first reported idea for Extended Reality was in 1838, when Sir Charles Wheatstone, a scientist, first described the concept of “Stereopsis,” also called “Binocular Vision.” This concept states the process through which your brain integrates two pictures. These pictures are each taken from one of your eyes and combined to produce a single three-dimensional image. As a result, the first-ever Stereoscopes were created, combining two pictures to create the appearance of depth in a third dimension. Likewise, today the Virtual Reality system uses the Stereoscopic display to give virtual visuals a sense of depth, improving the human’s interaction with a machine.
The First Part of the 1900s
Now let’s fast forward to 1935 and the era of publication of the “Pygmalion’s Spectacles.” These spectacles were published by an American science fiction author Stanley Weinbaum. In the book that this author published, the main character wears a pair of goggles to navigate through a magical universe. The emergence and production of Virtual Reality as we know it currently was initially predicted through this concept.
The Mid and Ending of 1900s (From 1950s to the 1970s)
We started to witness early applications of Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality technologies in the 1950s, 1960s, and 1970s, as follows:
- The first Virtual Reality device was invented by cinematographer Morton Heilig in 1956 and was marketed with the name “Sensorama.” To fully engage the spectator in the film, this cinema booth combined the three-dimensional, colored film into the stereoscopic format with sounds, fragrances, and a vibrating seat. In 1960, Heilig filed a patent for the world’s first (HMD) head-mounted display featuring stereo sound and three-dimensional pictures.
- In 1961, engineers and researchers from Philco developed the Head Sight head gear/headset based on Heilig’s concept. This was the world’s first Virtual Reality headgear with movement-tracking technology, made to be used in military services.
- Ivan Sutherland, a well-known computer scientist, also proposed the “Ultimate Display” idea during the 1960s. This was a proposal for a digital world that would be so convincing that the viewer could not tell it apart from the physical world or reality. The blueprint for contemporary Virtual Reality is commonly taken from this research paper concept.
- Ivan Sutherland, a professor at Harvard, developed the very first Augmented Reality headset in 1968. A forerunner of today’s augmented reality (AR) experiences, the “Sword of Damocles” headgear improved the device user’s perspective of the environment by displaying computer-generated graphics.
- MIT developed the Aspen Movie Map in the 1970s. A virtual tour of Aspen’s streets was made using images captured while a car was moving around the neighborhood. Yes! The map was generated through computer-generated routes and pictures to provide a complete map and tour of Aspen. For the first time, a Virtual Reality experience demonstrated how individuals could experience stepping into a virtual location.
The End of 1900s and Start of 2000s (From 1980s to the 2000)
The development of new technology to improve the Virtual Reality experience began during the 1980s. Jaron Lanier, one of the firm’s founders, is credited with coining the phrase “virtual reality” in 1987. Virtual Programming Learning Research Inc., the first company to market Virtual Reality goggles and gloves, was established in 1985.
Tom Caudell, a Boeing researcher, first used the term “augmented reality” in 1990. Then, in the early nineties, Virtual Reality arcade games like the SEGA Virtual Reality-1 motion simulator appeared. Furthermore, accessible Virtual Reality headsets for household use became available by the mid-1990s.
One of the first instances of augmented reality was displayed during the first live National Football League game, It featured the yellow yard marker, shown by Sports Vision in 1998. A yellow line was added to the live camera stream to represent the yellow yard marker. It completely changed the game and adding images over the actual scene swiftly caught on in other sports programming.
The Last Wave of Extended Reality Starting From 2010 to 2020
The early 2000s contributed little towards the development of extended reality (even though the 2007 launch of Google Street View may be considered a precursor to Virtual Reality since it enables users to travel to new locations.) However, Extended Reality technologies primarily started to take off around 2010. The following are some significant occurrences from this era:
- Palmer Luckey developed the Oculus Rift Virtual Reality headset prototype in 2010. The ground-breaking headgear rekindled interest in Virtual Reality with its ninety-degree range of vision and the utilization of computer processing power. After raising $2.4 million on Kickstarter, Luckey’s startup Oculus Virtual Reality was purchased by Facebook in 2014 for almost $2 billion.
- In addition, Sony and Samsung stated they were developing their Virtual Reality headgears in 2014, which was a busy year for Extended Reality. In the meantime, Google introduced its Google Glass Augmented Reality glasses, which overlay digital data onto the physical world and let users access applications like Gmail.
- This was the company’s first cardboard-based VR gadget and was a relatively low-priced cardboard virtual reality viewer built for smartphones.
- Then, in 2016, Microsoft unveiled its HoloLens head gears, which elevated the concept of augmented reality (AR) by fostering a more interactive and immersive experience for the users (thus, the term “Mixed Reality” came into existence).
- IKEA launched its IKEA Place application in 2017, which enabled customers to visualize furniture and other items in their homes for decorations and other purposes before making a purchase. We witnessed an earlier implementation of augmented reality in conventional retail.

By 2020, various businesses and companies had quickly embraced utilizing Virtual Reality, Augmented Reality, and Mixed Reality. We are witnessing the deployment of Extended Reality technologies in multiple fields such as manufacturing, instruction, healthcare, building, and even some federal law enforcement cases.
What Kinds of Extended Realities Exist in 2022?
Extended Reality has developed a lot during the past few decades. As we can see, the idea of this technology and the start of Extended Reality came into existence in the 1800s. After that, it only progressed and developed gradually. However, now we are in 2022, and the potential for innovation with the extended reality space seems limitless. Below is a breakdown of the most common kinds of Extended Realities trends in 2022.
The First Phase of Extended Reality Trends in 2022: Ongoing Hardware Innovation and Research in the Pursuit to Bring Full Immersion Technology
‘Immersion’ or ‘interactivity’ are words frequently used with virtual or mixed realities. When you access a virtual reality environment, you are placed in a completely new and unique world with some restrictions. Examples of these restrictions include limited hand tracking, limited surrounding area in the physical realm to move around, and much more.
When we feel wholly immersed in the virtual or digital world we are visiting, we have reached complete immersion. An infamous case of total immersion is in the movie “The Matrix,” where we are led to believe that reality or the physical world is a simulation. Although it is not the intended outcome, we might encounter a time of total immersion during which we maintain complete control of our virtual environments.
One might wonder, “How will we build this completely immersive virtual reality world?” All of this comes down to the tools we employ to access the virtual world or Metaverse. Modern-day tech giants such as Facebook, NVIDIA, Microsoft, and Unity work relentlessly to achieve total immersion through immersive hardware and interactive 3D-building software.
-
Headsets/ Head Gears and Additional Visual Elements
Headsets or headgear as we know them are one of the most frequently utilized hardware for experiencing Extended Reality. These headgears have evolved a lot during the past few years from their first launch, starting with its first attempt of the simple Virtual Reality head gears during the eighties and nineties to the now-used MetaQuest2, HoloLens2, and others.
Design and Technological Enhancements for Headsets/ Head Gears
When virtual reality gaming and training were initially explored and tested in the 1980s and 1990s, the leading Virtual Reality headsets we know currently were heavier and more noticeable. However, extended reality trends indicate that the fit and weight of Virtual Reality headsets will keep getting better as they have already become relatively lighter and unnoticeable. Another primary difference in modern-day headsets is wireless capability. Older headsets would have to be connected with a wire, whereas modern headsets do not require wired connectivity. Below are a few examples that will help you understand the difference in design from the previous headgear to the current versions.
Oculus Quest 2
Compared to earlier Virtual Reality headsets, the Oculus Quest 2 is lighter, more affordable, and offers incredible visuals within its 1080p display. Currently priced at $399, this headset is a much cheaper option than other headsets. One of the significant factors behind the success of the Oculus headsets is their affordability and versatility.
These headsets can be utilized with different platforms and are compatible with steam, which allows users to experience thousands of virtual reality games simply by connecting their headsets. The headset also features 3D audio, which adds a new level of interactivity within the virtual experience. In addition, the headset weighs only 503 grams, which is lighter than all its previous versions. Thus, the headset is extremely comfortable and can be used for long hours.
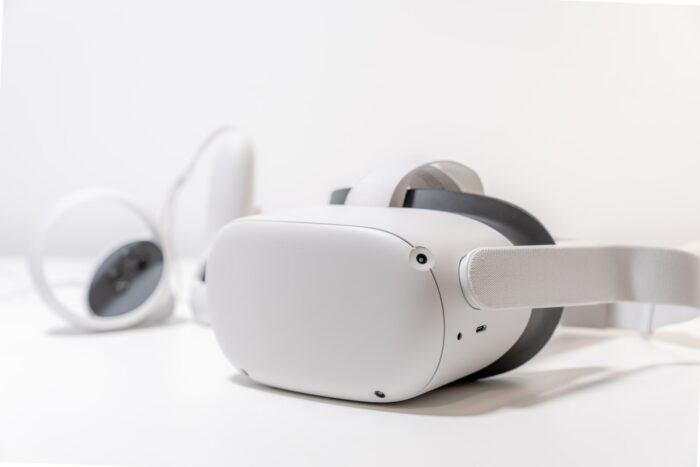

MeganeX
The Oculus feels like a full-size giant helmet on the head compared to the thin headgear we can view in Steven Spielberg’s Ready Player One adaption. However, the headgears in the movie are not implausible, even though it is a work of fiction. Launched in January 2022, the MeganeX Virtual Reality headgear was unveiled by Panasonic in partnership with Shiftall. The headgear is the same size as a small pair of sunglasses and barely weighs around 8 ounces.
However, these headsets are pricier than the Oculus Quest 2 and are priced at $900. However, their impressive 2560 x 2560-pixel display and 120Hz refresh rate is worth the price.
Sony PlayStation VR2
Widely known for its gaming stations, Sony has contributed immensely towards VR adoption by providing access to VR games and with their headsets. As a result, the PlayStation VR2 is swiftly rising to the top of 2022’s most popular VR gadgets.
“Participants will feel a magnified spectrum of experiences unlike anything else,” claims Sony’s Senior Vice President of Platform Experience Hideaki Nishino. “This is made possible by the inventiveness of the gaming realms produced by our high-end developers and the latest technologies integrated into the hardware.”
With cameras embedded into the headgear, this hardware tracks participants’ motions from the inside out and offers a 110 degrees complete view. In addition, modern and innovative gaze-tracking technology will monitor participants’ visual and head movements during games. Three-dimensional sound effects and real-time feedback from the headgear are additional features.
Mojo Vision
Mojo Vision’s contact lenses are the best example of the most advanced form of wearable tech. While these have yet to be released to the public, the technology will provide access to unhindered immersion simply by putting on a contact lens.
One of the strongest vocal objections against Google Glass in its initial phases was that users would have to wear the devices’ eyewear throughout the day to experience augmented reality. These contact lenses provide an excellent alternative, which is not bothersome to users and can be worn easily throughout the day. In addition, the lens offers users access to AR tech that would allow virtual images to be superimposed onto their physical surroundings in real time.
One of these lenses’ best benefits is that they also provide eyesight correction. Priced at $1500 for a pair, it may seem expensive to many, but given that it includes eyesight correction plus access to a virtual realm, it’s definitely worth the price.
Alternatives To VR Controllers
Similar to headsets, tech companies have also been working on enhancing VR controllers. While many headsets offer hand tracking, other exciting alternatives can assist with total immersion. For example, the sensors in the Oculus Quest controllers replicate your hands and their movements completely. In addition, the buttons and triggers on the Oculus Quest Controllers give more reactivity and manipulation.
To put things into perspective, experiencing VR and AR without controllers would be the most immersive way to experience alternate realities, especially for non-gaming purposes like educational and professional training. Gaming, too, can be enhanced using superior hand-tracking technologies.
Let’s explore other exciting alternatives for controllers.
-
Tactglove
Touch or Feel usage input/feedback is provided by Tactglove, created by bHaptics to give a more lifelike multi-sensory experience. Throughout their 10 Linear Resonant Actuators, the gloves offer clients a tactile experience. These gloves are perfect for training professionals such as surgeons and many others, where accurate and precise handling and control might benefit from this similar dexterity and response.
- Tesla Bodysuits
These bodysuits come fully equipped with state-of-the-art sensors that provide haptic feedback when an individual interacts with an object in the digital realm. In addition, the bodysuit can track complete movements; thus, controllers are no longer needed. However, since this is a relatively new concept, the bodysuits are extremely expensive and can cost up to $13,000. The company is currently working on creating affordable versions of this suit to make them more accessible.
Immersive Footwear Accessories
The environment in which you are standing is one of the most considerable barriers to achieving complete immersion. Even though your hands and eyes can transport you into the Extended Reality entirely, you can only move your legs far enough before you end up stumbling over your pet or knocking over a lamp or other things.
Treadmills
A treadmill that enables complete 360 degrees rotations might be the only answer to this issue. So you may engage in the activity or game of your choice once you are buckled in. Companies such as Spacewalk VR have also come up with excellent-quality treadmills. However, one big drawback is its exorbitant price of $14,800. Another issue with Virtual Reality treadmills is the amount of room they require. So a proper large space has to be dedicated to placing the treadmill.

Boots
EktoVR is another well-known business working on creating immersive footwear for Extended Reality. The goal of the company is to create a more suitable learning environment. They take the method of strapping a unique pair of footwear to your feet.
Your feet experience the same feelings as the virtually simulated world, all due to the efforts of EktoVR and their Ekto One Simulator boots. Your movements in the digital environment correspond to your steps outside in the physical world. So, despite the boots preventing you from moving, you will feel like you are moving.
The Second Phase of Extended Reality Trends in 2022: Retailers Accept Augmented Reality Mobile Application In-Store
Since most of the hardware still has a long way to go before reaching its full potential, complete immersion might not be possible for some while. But in 2022, you can count on merchants to set the extended reality patterns. For example, applications that use augmented reality were used by distributors and retailers to let customers try out their items before buying. Manufacturers and furniture designers also use Extended Reality technology to position sofas directly in your living room.
Expect clothes merchants to introduce such technology into their physical locations for users to access through their smartphones. For instance, Ralph Lauren claims that its virtual mirrors have a ninety percent interaction rate and are located in dressing rooms throughout its stores. In addition, the mirror provides details like sizes, styles, additional goods, and shop availability.
The Third Phase of Extended Reality Trends in 2022: For a Hands-On Learning Experience and Completely Interactive Learning, The Educational Industry Still Uses Virtual Reality

It has been noted that Extended Reality can profoundly impact individual retention. This is because humans learn by applying ideas to action rather than by remembering statistics and information. For example, imagine seeing the entire solar system in your living room while trying to learn more about the planets. You can zoom in, view it from different angles, and interact with the 3D virtual objects. This provides a highly interactive way to learn and can completely revolutionize the educational industry.
Home Education Is Not Going to be the Same Once More
Before 2020, most individuals would have needed help understanding the concept of homeschooling. However, now that almost all parents have gone through this experience, many are wondering if there is a way to maintain the social advantages of having their children attend school and classes with other peers while protecting their child’s health and wellbeing.
The Optima Classical Academy is one institution that wants to help kids enter the Metaverse. To start a Virtual Reality program in November 2022, the Florida charter school intends to give students approximately 1,300 Oculus headsets. Youngsters will be able to engage and converse with one another as they already do in an actual physical classroom thanks to this program, making this one of the first implementations within the educational sector.
Adult Education
One of the biggest challenges to continuing adult and vocational learning is time. You already work full-time, and it would take too long to get to campus to attend one course. However, a digital campus with practical education can enable many of us to continue learning. You can attend classes no matter where you are, and instead of sitting through a boring zoom call, you can put on your headset and step into the classroom itself.
The Fourth Phase of Extended Reality Trends in 2022: Workplace Training is Shifting towards Extended Reality
Most businesses/ companies and institutions are now utilizing digital/ virtual learning to train their staff personally. This is not limited to only engineering or business fields; the medical sector and others also fully use virtual environments to train their staff.

Walmart
To recreate the level of customer service and client relations, Walmart staff is currently receiving training in virtual reality. It is all about getting the opportunity to feel what it would be like to be in somebody else’s shoes and experience it all before it occurs, says Heather Durtschi, Senior Director of Learning, Content Design, and Development at Walmart.
Extended Reality, or to be specific Virtual Reality training, is not just being used by Walmart. For example, virtual reality technology is used by BMW, FedEx, and Bank of America to train their staff members in designing, prototyping and developing, and package handling techniques, opening accounts, and improving customer support and relations, respectively.
Extended Reality training does not just apply to businesses that serve customers. For example, law enforcement organizations have made their way into the Metaverse and are using Extended Reality to its fullest. Officers are placed in high-stress scenarios through VR simulations without the threat of catastrophic damage or physical injuries to the officers. They are trained professionally to handle any situation they might face in the physical world.
FLAIM
For firemen, FLAIM provides an immersive and interactive training program. The system comprises a headgear, a heat suit integrated with the haptic technology and temperature management, a backpack and breathing device to record tiredness and rate of breathing, and a tube and nozzle that offer correct resistance when utilized in the simulation. This mechanism as a whole is a miracle of extended reality that reveals the future to us. It also helps the firefighters to train appropriately for their “on-field” work.
Raytheon
A pioneer in aerospace, security, and other production, Raytheon currently delivers a training method that allows “trainees to engage with objects in their physical surroundings while still engaged in a virtual reality world,” after utilizing Virtual Reality in intensive training for many years.
The Fifth Phase of Extended Reality Trends in 2022: Mixed Trade Presentations Developed from Computer-Oriented and In-Person Experiences
Every time we begin to believe that physical products and services are prepared to resume taking place face-to-face as they once did, we are confronted with a new variation of diseases that pushes us to reconsider networking events as a whole. For example, the COVID trade fair engagement has so far alternated between physical, face-to-face events with safety precautions (such as using masks, inspections, and distance between exhibitors) and virtual events accessed via a laptop, computer, or smartphone. These digital interactions include discussions, presentations, primary addresses, accessibility to published statistics, Public Relations, and other show-related media that the producers give.
Improved Physical Interactions Between Individuals
Trade events have the potential to progress past the current mixed show and enter Extended Reality. Companies and event planners can rely on Augmented Reality projections for data on the showroom floor for attendees who will be there in person, allowing visitors to examine and evaluate goods without having to touch them. In addition, attendees can access data directly on their smartphones by gesturing to specific locations of each stall or program.
Immersive and Interactive Experience at Residence
If you decide to watch the program from home, the planners can build a conference hall in virtual reality so that consumers can explore the event as if they were there. Customers have access to items, live demonstrations, and even the ability to interact with selling and promotion staff. Customers at residence shouldn’t feel that they are missing out on the entire industrial exhibition experience. Finding a place for cocktails and socializing beyond hours is possible.
What is VR?
Virtual reality (VR) applications employ headgear to submerge users in a digitally created environment completely. In addition, these headgears provide lifelike sounds and sights that appeal to the senses to create an immersive virtual environment. Using controllers, individuals can move around these virtual worlds and can interact with other users and work, shop, play and much more.
What is MR?
Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality are both subsets of mixed reality (MR). It combines the physical and digital realms to produce intricate landscapes where physical and digital elements may communicate in real-time. As with Augmented Reality, you can see your surroundings, but the headgear creates three-dimensional visuals with depth and interactivity, as in Virtual Reality. It overlays virtual material over a real-world environment, much like augmented reality. Much like virtual reality, this interactive content allows users to alter the digital items in their actual location. If you are looking for more details on Mixed Reality, then you can refer to our article explaining all details about Mixed Reality.
What is AR?
Instead of submerging users, Augmented Reality (AR) uses a device, often the camera on your smartphone or tablet, to superimpose digital images and sounds onto a physical world environment. As an illustration, when watching a live sporting event, you could notice replays or interviews on video or a digital statistic overlay hanging over the participants. If you’d like to learn more about augmented reality, you can view our article on Augmented Reality, where we discuss the versions of augmented reality, its applications, and everything else.
Main Differences
The technologies covered include Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), and Mixed Reality (MR), which are the subfields of Extended Reality. So, let’s discuss the differences between AR, VR, and MR. From the following examples regarding each Extended Reality technology and a brief description, you can understand the difference between Augmented, Mixed, and Virtual Reality.
Mixed Reality
A combination of Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality is called Mixed Reality. It fuses physical and digital elements to let users create new worlds and visualizations. Here, individuals can interact with virtual objects in real time by touching and moving them around. Interacting with these elements is not possible within VR or AR. One of the most prominent reality gadgets is Microsoft’s HoloLens2.
Mixed Reality gives the best of both worlds with this combo. Here is an illustration of how it operates: While Mixed Reality still uses a headgear, similar to Virtual Reality, to observe the world via a transparent viewport or glass, it can simultaneously display images on top of the surrounding environment.
The interactivity of Mixed Reality and the lifelike representation of the projection it adds to the environment set it apart. Instead, users may engage with the immersive material using their own natural body and finger motions rather than relying on phone displays or remote controls.
The leaders in Augmented Reality technology are now Apple and Google. However, Microsoft’s HoloLens and the heavily backed Magic Leap, now in development, have gained much momentum within the Mixed Reality space.
Virtual Reality
Virtual reality (VR) is a term used to describe an experience that completely submerges the user in a digital environment and removes them from their surroundings. Popular entertainment gadgets like the Oculus Rift, HTC Vive, or Google Cardboard are the earliest examples of Virtual Reality equipment. Users can browse a variety of digitally created or recorded environments.
For example, it may include using an awesome sword to slay a ferocious dragon or soaring through space. In addition, virtual reality users can look around with a 360-degree field of vision, making them feel like they’ve truly stepped into another universe. With the introduction of Google Cardboard in 2014, Virtual Reality experienced tremendous growth. Within months, Samsung and Oculus joined the race.
Another critical factor in improving healthcare is virtual reality. Patients who underwent dangerous surgery the day before may now climb in the Alps while lying in a hospital ward. Do you wish to feel like a marathon runner when you have asthma? You can also experience it all, even with your asthma. Beyond science fiction, clinical researchers and medical professionals have also begun investigating the beneficial impact of Virtual Reality on patients’ life and the job of medical professionals.
Virtual Reality can also be used in physical treatment to shorten the healing times. The usage of games like reality in real-time treatment, such as for patients in Neuro Rehab Virtual Reality, showed increased patient involvement and, as a result, a substantial enhancement in mobility.

Augmented Reality
Augmented Reality integrates digital components into a live image, frequently using the camera on a smartphone and a pair of glasses. Pokémon Go, Snapchat lenses, and home architecture and design apps are examples of recent augmented reality applications.
It is anticipated that using augmented reality in healthcare would produce revolutionary benefits. Augmented Reality, which has gained recognition as among the most potential implications of digital medical technologies, is expected to improve healthcare and standard medical practice for patients and medical practitioners.
One such instance is AccuVein, which makes life easier for nurses and patients by using Augmented Reality technology to assist nurses in finding veins. A little more than forty percent of intravenous injections (IVs) bypass the vein on the first attempt. This percentage rises for young and elderly children if augmented reality is used.
AccuVein displays augmented reality (AR) images over the skin using a portable scanner to reveal the location of veins in patients’ bodies. As a result, locating a vein within the first needle jab is now simpler and faster than ever. As a result, all people’s access to healthcare is improving because of new Augmented Reality ideas and technology.
Due to recent developments, more businesses have begun considering utilizing augmented reality (AR) technology. As a result, it has become more accessible, inexpensive, and usable to provide more vital tools for education, communication, and healthcare to enhance results.
So, Virtual reality (VR) is a wholly immersive and interactive digital atmosphere. In contrast, Augmented Reality (AR) is a perspective of the physical world with an intermediate overlay of the virtual world. Finally, mixed Reality (MR) provides the most immersive experience with a view of the real world or physical world with an overlay of a virtual world where physical and virtual identities and objects can interact.
What are the Main Applications of Extended Realities?
The possibilities are endless, and new horizons will be revealed by imaginatively fusing Extended Reality technology with human imagination. Nevertheless, a few Extended Reality applications have significantly impacted society. Below are vital applications of Extended Realities that you will find in everyday applications.
Games and Entertainment
While Extended Reality for entertainment and gaming may seem trivial, they comprise a large market. For example, the Extended Reality games market is expected to reach around $18 billion by 2023.
Players can experience the picked scenarios as closely as they would in real life, whether traveling to a different time or location or discovering spectacular future settings. In addition, from the convenience of their Virtual Reality headgear, users can also virtually witness live music performances and athletic activities.
An increasing number of game developers are releasing virtual reality games. Additionally, virtual reality gaming will likely continue to advance very inventively, considering how fiercely competitive and engaging the gaming business and the games are.
Healthcare
Many fields, including mental health, physiotherapy, pharmacological production, and training for healthcare workers and patients, are seen as potential applications for VR and AR technology in the field. The use of technology also facilitates collaboration, particularly between numerous facilities. For example, doctors widely used Extended Reality to provide distant care throughout the pandemic.
Extended reality is widely used in medical image processing technologies, including CT scans and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Instead of conventional two-dimensional imaging, it provides employees with complete three-dimensional depictions of human bodies. As a result, medical professionals may make diagnoses more accurately because they can visualize the important structures more precisely.
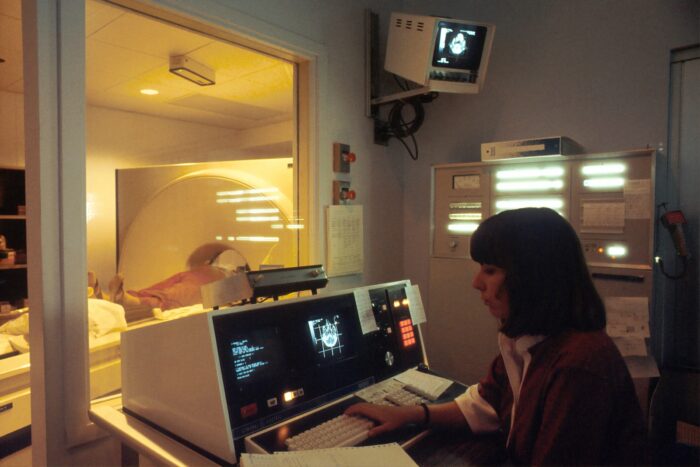
Among the applications of Extended Reality that stands out is surgical training. Immersive simulations enable medical professionals to develop sophisticated surgical and medical procedures or start learning basic surgical approaches without endangering patients’ lives. Medical professionals can use augmented reality (AR) to make smarter decisions and give their patients more enlightening suggestions during live procedures or patient care. Individuals can participate in a controlled setting where they can confront and safely transcend their phobias through medical Virtual Reality treatment.
Engineering and Manufacturing
A trained staff is now required to stay ahead of the competition in the fast-paced business environment, making training an essential yet costly task. Extended Reality tools can help you save money and time and avoid accidents.
A perfect use application for computer-aided design (CAD) is the ability for designers and their customers to immerse themselves in actual life-size creations while sketching/ drafting, or designing. This makes it possible to explore the design parameters better and finalize the design required.
There are instances when risky operations are required in engineering and manufacturing learning and working environments. Thanks to augmented reality, workers can perform these tasks while working at a safe distance. For instance, a worker can instruct a robot to carry out some operations involving risky chemicals under their supervision and stay at a distance to watch the task performed without directly contacting the substances themselves.
Novice factory workers can learn how to operate dangerous equipment through simulations while staying at a safe location without being present on the machine. Job simulators can include exact deadlines, obtrusive interruptions, and other urgent requirements to teach workers how to work in factories.
Assembly, quality assurance, and maintenance are further procedures that Augmented Reality can help with. In addition to viewing and receiving data on mobile phones, headgear, or other augmented reality devices, workers can also receive verbal and visual directions. In addition, it may contain specific technical information, such as coverings or limitations. Augmented Reality is used to increase productivity at essential points in the production process by companies including Boeing, Porsche, and Lockheed Martin.
Food
There are many different types of food products. Extended Reality provides a fresh way of thinking and performing, whether through broadcasting educational content, digital food manufacturing procedures, or simulation of real-life situations. For instance, several restaurants currently have tablecloths that may be used as gaming consoles and cookbooks.
Appropriate cleanliness in food facilities is among the most crucial elements of food manufacturing. Unfortunately, human mistakes or an absence of supervision can occur during manual testing and maintenance. Adding a virtual layer to any operation or maintenance, such as a regular hygiene inspection, is now available with mixed reality tools like the HoloLens. The virtual layer can cover all crucial sections, which might draw attention to places that go unnoticed with manual operations.
You can even incorporate a no-mistake function. This can prevent an employee from proceeding to the next stage unless all prerequisite tasks have been fulfilled. The capacity of HoloLens to capture information and preserve it in a database also means increased traceability of cleanliness inspections, a significant area of attention for food producers.
Because Virtual Reality learning has been proven to be very effective for individuals at retaining information, it is most likely to be used in the workplace. It is already being increasingly used in some businesses, which boosts productivity. Sophisticated processes can be reduced to simple elements to ensure that even newer employees can understand and produce consistent, upgraded quality outcomes.
Any production-related job can be realistically duplicated using Virtual Reality, and it can provide insights into the worker’s speed. Additionally, since Virtual Reality learning does not require assistance from coworkers, new hires can be instructed without existing employees having to set aside time to teach them. Finally, a worker should be able to understand the future stages using visual guidance.
eCommerce and retail
Both physical commerce and internet commerce industries benefit immensely from Augmented Reality. Consumers can conveniently learn everything there is to know about things in stores. You may immediately get feedback and suggestions by directing your camera to an Augmented Reality enabled object. While identifying purchase trends from the data, merchants can also give promotions through this channel.
For online shopping, augmented reality (AR) makes the experience more like going to a store in person. This was particularly helpful to stores during the pandemic. Most consumers prefer to try a product out before making a purchase, which is made possible by this technology.
Customer returns in the eCommerce sector account for up to 550 billion dollars annually. Unfortunately, it frequently happens that people end up purchasing an item depending on a stock image, only to discover it is different from what they had expected. This annoyance is removed by Augmented Reality technology. Customers can decide whether they would enjoy a product by letting them test it out in augmented reality.
The “experience before you purchase” augmented reality product visualization utilized by retail behemoth Macy’s assisted the corporation in lowering return rates to under two percent. Shoppers may now enjoy interactive shopping experiences at well-known retailers like Saks and Saatchi.
According to studies, forty-seven percent of buyers said immersive technology helps them “experience more involvement with things” when purchasing online. Augmented Reality enables a person to interact directly with a product in a virtual setting rather than limiting them to envision how it will appear.
Education
According to research by the National Education Association, whereas reading and lectures both have learning retention rates of only ten percent and five percent, respectively, Virtual Reality has been proven to have a seventy-five percent learning return rate. Immersive technology can make education much more interesting than just reading a text or viewing a clip.
Augmented reality provides students with practical, physical world experience without having to set up for a traditional classroom. For example, it allows users to practice surgery on fictitious patients, experience life in space, or even watch all the mechanics of machines in engineering. Unique learning opportunities are provided by Extended Reality, which is anticipated to have an increasing impact on learning at all levels, from elementary to secondary and higher secondary to professional.
Virtual field trips are possible using Extended Reality, including visiting places you can’t physically see. Additionally, you can examine intricate scientific subjects in great depth, such as altering a three-dimensional model of a molecule. In higher secondary education, Extended Reality makes remote, self-paced learning possible. Any subject, from space learning to biology or engineering, can stimulate students’ senses in multiple ways. The information is more memorable when the connections are richer. Augmentation reality for games, which turns courses into games, might improve learning results even further.

Real Estate
Even if the purchaser and seller of the house are on different ends of the world, real estate brokers can give potential purchasers a preview and walks of properties as if they were seeing them in reality. For usage with smartphones or headgear, you can create advertising, product demonstrations, and showcase open houses. With the present capabilities included in some internet browsers, some real estate brokers are already taking advantage of these opportunities.
Workplace
New employment practices have been done due to the epidemic, including hybrid employment and remote workers. Executives view extended reality as a valuable tool for reuniting workers. Additionally, it opens up new possibilities for work training, assisting workers in learning as they go and gaining practical experience in a secure setting that will make them more effective.
The world’s largest logistics company, DHL, launched its Google Glass-dependent Vision Picking Program in its facilities across nine nations. They reported fifteen percent increase in productivity thanks to more precise and effective fulfillment. Lloyds Bank is also investing in Virtual Reality technology to train their personnel in transferable skills. They envision that this technology will help them understand how to cope with challenges and manage stress.
Defense
Extended Reality can also alter how soldiers are prepared for battle and behave while engaged in it. Gen. James McConville, commander in chief of staff of the United States Army, states that he and his team are enthusiastic about Extended Reality.
Since its creation, the United States Army has spent millions of dollars on Extended Reality technologies. For example, the Integrated Visual Augmentation System (IVAS), which mixes a subset of the training settings with actual data to improve combat readiness and performance, has been purchased by the Army and the Marine Corps. Similar to it, Extended Reality technology has been used by the Navy and Air Force to educate their jet pilots.
The United States Defense Department is quick to hail the limitless potential of Extended Reality advancements for significantly better teaching, spatial awareness, logistics support, combat preparedness, and even medical training and protocols. Extended Reality can give training far more quickly and inexpensively in many instances than traditional training. For example, the United States Air Force has cut the length of flight school from twelve months to four months by utilizing virtual reality (VR), artificial intelligence (AI), and biometric surveillance.
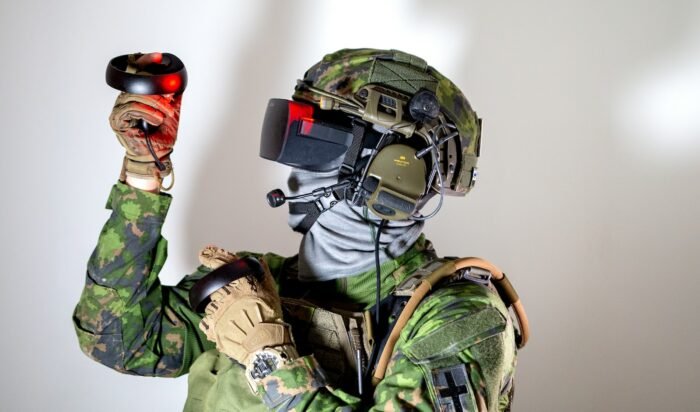

Using Extended Reality technologies, military service members can train and practice for expected combat situations. They’d be able to learn how to know the position and whereabouts of friendly forces or disclosed dangers and even overlay digital foes and hurdles as required for good planning and preparation for the actual battle. By incorporating additional digital data from a physical world perspective, military personnel can conveniently explore any global landscape.
Travel and Tourism
The unusual and terrible epidemic negatively influenced almost all areas of the economy, with the transportation and tourist sector particularly heavily struck. According to the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD), the substantial drop in international travel caused by the epidemic has reduced the global Gross Domestic Product by more than four trillion dollars.
Intelligent operators are leveraging extended reality to provide stay-at-home vacation opportunities and adventures because so many individuals are unwilling to go. However, both customers and the tourism sector stand to gain immensely from this technological revolution. Extended reality travel allows customers to see the world safely and for much less money. Additionally, this technology gives businesses having trouble making ends meet a new source of income.
For instance, the Petra Xplore Application was made available by the Jordanian government. Which allows users to teleport to the UNESCO World Heritage Site using virtual reality technology. There are exciting places that guests can stroll around and explore. The narration explains the historical value as people tour the city. According to industry analysts, extensive reality travel is expected to remain popular with travelers. This is perfect for those searching for a cheap way to see the planet even after the outbreak.
Extended Reality Technology
Let’s first examine what extended reality (XR) training is to fully comprehend what an Extended Reality System (XRS) is capable of. Instruction in extended reality (XR) includes virtual, augmented, and mixed realities interactive and immersive training technologies. This kind of instruction “extends” reality by putting students in a secure, multimodal learning setting that mimics actual training circumstances. This technology applies to students and official field workers such as construction workers, engineers, medical practitioners, and more.
An Extended Reality System (XRS) is one option businesses have for managing, delivering, and assigning this training to their employees. Organizations may easily manage their Extended Reality data, materials, and clients from one practical platform using the technology of an Extended Reality System. This employs cloud-based application programming interface technologies. The primary objective of an Extended Reality System is to simplify the management of Extended Reality training. Thus enabling users and customers to utilize Extended Reality to its full potential.
Let’s look at each of the sub-fields of Extended Reality: Augmented Reality, Mixed Reality, and Virtual Reality, and their technologies separately.
Augmented Reality Technology
Augmented Reality is an incredible technology combining real and virtual words. But knowing how the technology works is essential. So, let’s have a look at how Augmented Reality technology works.
Computer vision first determines what is in the user’s immediate environment from the information in the camera stream. As a result, it can display online material pertinent to the user’s current search. The rendering process involves showing this digital stuff realistically so that it appears to be a component of the actual environment. Let’s use a real example to clarify this before going into further depth. Think of utilizing a genuine piece of cardboard as the physical basis for a board game. This concept combines augmented reality with real life. Keep reading to understand Augmented Reality technology.
The cardboard box is first recognized by computer vision after it has processed the camera’s raw picture. The game started with this. To ensure that the Augmented Reality game properly coincides with the cardboard box, the rendering module adds the Augmented Reality game to the original frame. The three-dimensional location and orientation of the cardboard, as assessed by computer vision, are used for this.
All of the following must occur every time a new frame from the camera is received since augmented reality is a live technology. With most current smartphones operating at thirty frames per second, we have just thirty milliseconds to do this. We often fail to realize that there are a dozen processes involved in making this happen. The the view that you are able to see is frequently delayed by around fifty milliseconds to enable all of this to happen.
Mixed Reality Technology
The changing dynamic between people and robots significantly impacts mixed reality. For a Mixed Reality solution to function well, it must be able to comprehend the environment. It also predicts human movements within the place.
Mixed reality combines a variety of cameras, sensors, and frequently Artificial Intelligence-enabled technologies to process information about an area and utilize that data to generate virtually improved experiences.
An excellent example is when a person dons a set of mixed reality eyewear or glasses. The cameras and sensors in those eyewear/ glasses integrate into a software program. This program gathers as much data about the surroundings as possible, basically building a digital map of the actual world.
It is important to keep in mind that due to its high price, mixed reality is currently only accessible to large businesses such as Kawaski and Heinz, where the technology is being used to improve overall efficiency.
Projecting Holograms
By utilizing a preexisting database, mixed reality technology may enhance the environment by projecting holographic pictures and content into the world. The following are included in mixed reality technology:
- Environmental and Surrounding Recognition: The capacity to map an area and overlay data onto that location in a way that combines digital and physical world identities and objects.
- Human Existence and Cognitive Acknowledgment: Mixed Reality technology relies on sensors and cameras that monitor humans’ gestures, voice, and inputs.
- Spatial Voices and Sounds: 3D audio and sound experiences created to enhance the realism and immersion of digital encounters.
- Positions and Locational Awareness: The capability of Extended Reality technology to recognize both its position and angles and the user’s position and the location at any given time.
- Three-Dimensional Resources: Content that is entirely three-dimensional and usable in the physical world. These resources are frequently referred to as “holograms.”
Mixed Reality must be capable of tracking the following data to function properly:
- Areas, surface type, and limits of objects (through scene acknowledgment and spatial mapping)
- The posture and motions of a person’s body in rest and motion
- Things and places in the real world
- Environmental sound and illumination (for added realistic effects).
The ability of Mixed Reality solutions to seamlessly blend the physical and digital worlds extends beyond the fundamentals of augmented reality technology. This is due to computer processing on the cloud, sophisticated input sensing, and ambient perceptions.
Virtual Reality Technology
The sensors of a Virtual Reality user are stimulated using devices for Virtual Reality technology. These may be applied on the body or directly by the user. Sensors are operated by Virtual Reality technology to detect motions, such as button pushes and controller movement patterns involving the hands, head, and eyes of the operator.
The freedom to move about in space when using a Virtual Reality headset is a crucial worry. Virtual reality (VR) uses the words inside out and outside in tracking. In both instances, it’s discussed how the Virtual Reality system would keep track of the operator’s and their accompanying gadgets’ whereabouts as they move around a space. The location of the operator in relation to the environment is tracked by inside-out tracking systems. Examples include the Microsoft HoloLens, using a camera mounted on the headgear.
The equipment’s sensors turn the power from a push button or hand motion into an electrical signal. Then, the signal is sent to a computer or other machine for processing.

Virtual Reality Devices
- These are the pieces of hardware that make VR possible. They consist of personal computers, which handle operator inputs and outputs, gaming consoles, and cellphones.
- A few examples of input devices are virtual reality (VR) controllers, tracking balls or balls, sensor wands. Other wearable electronics like data gloves, tracking pads, control buttons, movement trackers, electronic bodysuits with sensors, treadmills, and motion platforms (virtual Omni), which use pressure or touch to generate power that is then converted to a signal to enable selection from the operator to the three-dimensional environment. Users can utilize these to traverse three-dimensional environments.
- For optimum quality and experience, the computer should be able to generate high-quality graphics, commonly accomplished using graphics processing units. To speed up the production of pictures and graphics in a frame buffer and for the display, the Graphics Processing Unit is an electrical component on a card that receives data from the CPU and tries to control and modify memory.
- Visual, auditory, or haptic displays are examples of output devices that elicit a sensation from consumers by presenting them with virtual reality (VR) material or environments.
- The team at Meta is also working on creating ‘robotic’ skin. This would allow users to feel the sense of touch in the digital realm through haptic feedback. This would allow users to fully experience interactions within the virtual realm. Imagine playing basketball and feeling the ball when you hold it. Once its ready, this particular innovation could revolutionize the way users interact within the Metaverse.
Virtual Reality Headgears
A virtual reality headgear is a head-mounted small helmet or eye cover-like gadget that projects virtual reality images into the user’s field of vision. A Virtual Reality headset also includes a visual display or screen, lenses, stereo sound, and motion tracking sensors or cameras to detect head or eye motion. Sometimes, it also has built-in or linked controls for navigating the Virtual Reality library.
- Gyroscopes, structure light vision-based devices, magnetometers, and accelerometers are some examples of sensors that may be used to detect and monitor eye or head movement. In addition to delivering advertising advertisements, sensors may be utilized to lower the rendering burden. For instance, the sensor detects the user’s gaze location and then reduces rendering resolution away from it to save demand.
- In addition to the screen resolution, frame rate, optical quality, and field of vision, image clarity is influenced by the camera quality. For example, the camera is also utilized to track movement when a user travels around a space in a virtual reality session. However, due to the considerable latency that cameras often produce, sensors are a better choice.
- The positioning of the headgear with respect to the surroundings is determined by sensors or cameras installed in the room atmosphere outside in systems like the HTC Vive.
- In general, there are three categories of virtual reality headgear: entry-level, middle-range, and high-end range gears. Cardboards used with smartphone devices are considered low-end. High-end Virtual Reality headgear like the Personal Computer tethered, and cordless HTC Vive, Valve, and Oculus Rift fall into the middle range category and include products like the Samsung mobile Virtual Reality Gear Virtual Reality with a specialized mobile computing device and PlayStation Virtual Reality.
Virtual Reality Software
- Oversees the operation of the Virtual Reality output devices and input devices evaluate incoming data, and produces appropriate feedback. As a result, the Virtual Reality program needs timely inputs and needs to respond quickly with its output.
- A Virtual Reality developer can use a software development kit from a provider of Virtual Reality headsets to create their own Virtual World Generator (VWG). A Software Development Kit offers fundamental drivers as an interface to contact visual rendering libraries and access tracking information. For specific Virtual Reality experiences, Virtual World Generator is fully prepared and readily available without any issues.
- Virtual Reality material is managed by Virtual Reality software, which transmits Virtual Reality content from the cloud and other locations through the internet.
Virtual Reality Sounds
Some headgear includes their personal built-in sound headset. Others allow you to use headphones as an additional gadget. A three-dimensional illusion of hearing is accomplished in virtual reality sounds. This is done by employing positional, multiple-speaker sounds, often known as positional sounds. This gives operator-specific cues to attract their attention or even provide data to the gadget operator. This technique is currently widely used in surround sound systems in home theaters.
The Competencies and Functionality of an Extended Reality System
Although features differ from platform to platform, the application where the Extended Reality technology is being utilized differs. For example, an Extended Reality System often allows an institute, organization, or business to carry out a mix of the tasks given below:
- Assigning and delivering without delay or bottlenecks for Extended Reality elements to any user or gadget.
- Incorporate and connect with an already existing learning administration and control system to seamlessly track and gather important training metrics, such as user progress, a choice selection of the products, and eye and body movements.
- Creates customized Extended Reality training using associated software packages
- Updating the Extended Reality training over Wi-Fi without the user needing extra software or manual control.
Extended Reality Pros and Cons
There are many rising technologies worldwide, and Extended Reality is one of them. However, each machine, equipment, and technology has drawbacks and benefits. Here, we have combined a few pros and cons of Extended Reality that might be beneficial for you to understand the technology more deeply.
Pros
Extended Reality technology offers a different digital and physical world than what we are used to. This technology provides not only new advances in the technological world but also brings many advantages that many of us might have never thought about. Mixing the real world with the virtual world is not easy, but it is possible with Extended Reality. So, here are a few advantages of using Extended Reality in our lives:
Upgraded and Effective Visual Training Environment
As mentioned earlier, training can be more effective with Extended Reality technology. Students can see the material through three-dimensional models and graphics. In addition, extended Reality allows students to see, sense, and experience the subject matter. This is helpful in training, especially in the field of healthcare.
It aids in students’ knowledge of concepts and procedures. According to studies, visual aids enable students to digest knowledge more quickly and remember it for extended periods of time. Think of difficult equipment training, for instance. This helps in properly preparing workers for using the equipment in the field. Extended Reality lets trainees view three-dimensional representations of the machines, explore individual pieces, and learn more details about each component. This results in the workers properly handling and using the devices to their total capacity.
Bringing a Safe Training Environment
High danger levels can be present during real-world training exercises; one mistake could have catastrophic repercussions. However, adopting Extended Reality technology in training reduces the possibility of endangering people or expensive and specialized equipment. While providing a secure environment for students/employees to train. Employees or students can fully participate and confidently do this without being concerned about the results of their actions. This allows them to make mistakes freely and simultaneously learning from them and finding solutions to their problems. It enables training participants to practice as frequently as required. They can then familiarize themselves with the processes and safety guidelines, and refine their abilities without causing any damage.
For instance, a little scalpel slip during practice on an actual patient during medical school can result in severe damage or much worse situations. However, by using Extended Reality technology, the students can repeatedly practice surgeries and other risky procedures in a digital setting. This would suffice until they are confident enough to perform them without harming any living individual.
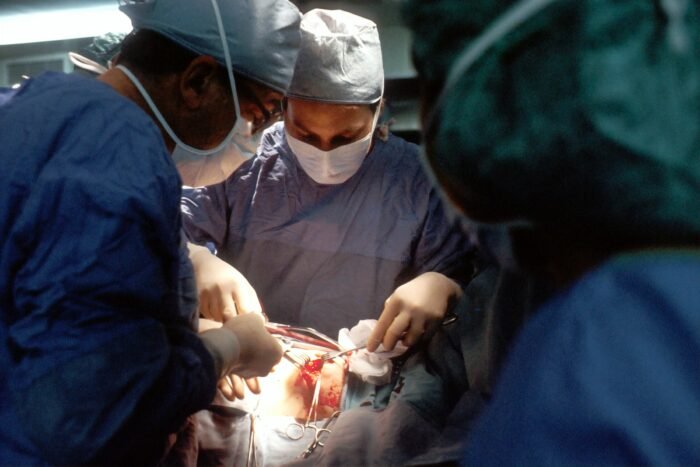
Improvements in Work Engagement and Training
With the help of completely interactive simulations made possible by the Extended Reality technology, employees are more entertained and engaged throughout the training. The same is the case with students who find watching movies fun. This is a better way to learn as compared to reading dated books. Extended Reality can make learning in schools fun for such peers.
Lifelike images and the intense immersion level increase learner engagement. Let’s face it, learning through interactive simulations and activities doesn’t feel like a job. The standard materials turned into Extended Reality gaming materials make learning exciting and entertaining. This encourages learners to take an active role in training events. As a result, they would be more inclined towards finishing assignments while still being competitive throughout the sessions.
Improved Employee Retention Rates and Successful Business
The levels of effective learning are significantly increased by immersive, visually stimulating instructions and teachings. Furthermore, in contrast to conventional training approaches, “learning by performing or experiencing” aids memory retention. This increment in the retention rates of employees is better for businesses. Similarly, if students are considered, the average student dropout rate can decrease significantly through the introduction of Extended Reality learning. Simply put, Extended Reality has the potential to reshape the training and education industry completely.
Unmatched and Strong Analytics and New Metrics
Data technologies, improved analysis, and new parameters are made possible by Extended Reality training technology. Extended Reality technology uses sensors to gather valid real-time data about people’s behaviors, eye movements, gestures, body language, surroundings, and more. Organizations, Schools, or Businesses can evaluate the training program’s success and pinpoint its weak points with these parameters. Firms can use this to track training progress, employee engagement levels, and program weaknesses. This can help them ensure that the training program is successful and produces the desired results. Then, they can work on improving the weak parts, eventually increasing the success rates of their learning programs. Thus enabling them to get their desired results without much effort.
Collecting training or instructional parameters for all the employees or students in a setting can take time and effort. However, organizations can use an Extended Reality technology to automatically collect essential performance indicators. Such as attempts for task completion, the total number of tasks completed, and scores achieved for each job. This is evaluated for each individual participant in the training and presented on simple dashboards for additional analysis.
Providing Extended Reality Training to Devices Effortlessly.
The Extended Reality technology can efficiently work over the cloud, making the transfer between devices over the internet quite simple. An Extended Reality technology can remotely distribute training tasks or lessons and updates to Extended Reality devices. This can be done over a simple internet connection. No manual access to the Extended Reality devices or accessing any software is required. A simple command is enough to upgrade an Extended Reality device with the settings, material, or anything you want.
Although every system is unique, this technology normally enables businesses or organizations to designate training or tasks. This allows enterprises more flexibility, versatility, and management over the unique learning routes of their employees.
Cons
Every technology in the world has its drawbacks. Similarly Extended Reality has its own disadvantages. The following are the disadvantages that you may find in Extended Reality technology:
Exorbitant Costs
Although it does have a price, Extended Reality technology provides a rewarding, dynamic, and exciting platform for training employees. However, purchasing the Extended Reality hardware and constructing the preliminary stage software can be costly. Organizations and Businesses on a tight budget may find investing in Extended Reality technology challenging because setting it up and running it in the workplace can grow expensive with the time. The upfront fees, however, are more than made up for by the long-term financial advantages. Additionally, Extended Reality is slowly becoming cheaper and more accessible for everyone thanks to technological improvements. However, maintaining the Extended Reality technology and running it for up-scale projects can still be costly for some.
Probable Health Threats
As we all know, Extended Reality technologies use their own devices, mainly consisting of head-mounted devices (HMD). However, it also includes entering the virtual world and forgetting the real world. So, the long-term usage of Head Mounted Devices has been reported to cause severe headaches, nausea, and eye pains in some individuals. In addition, too much time spent in the virtual world can make some people queasy. Forgetting about the real world can result in detachment from the real world. This could cause disturbances in relationships and surroundings of the person.
Being a Rigid Technology
The versatility and adaptability of a conventional approach need to be improved in Extended Reality based workforce training. Students are free to pause and ask questions at any time in a traditional setting. However, when it comes to training through Extended Reality, it is challenging to interrupt the training. Because Extended Reality training programs are created to ensure training completion in a particular time frame. This is generally, already set within the device or software that you are using. Since everyone’s capacity for understanding information differs, it could be a significant problem when learning through Extended Reality.
File Size and Wi-Fi Can Have an Impact on Content Delivery and Upgrades.
Advanced functionality and more comprehensive Extended Reality training programs may have a detrimental impact on information downloading times. Low speed and bandwidth Wi-Fi may also prolong the installation and updating processes. Businesses planning or already using the Extended Reality technology should ensure the necessary training material is already downloaded onto the Extended Reality device they will be using. Companies should do this before the start of the session to avoid this issue. As it may cause long delay times during your training sessions or usage of the technology.
Variations in Compatibility between Devices
The operating systems and devices that each Extended Reality is equipped with vary. Before their training begins, businesses should ensure that their Extended Reality technology is compatible with the hardware, software, or existing content they use for learning. We all know that each Extended Reality sub-category has its glasses, devices, and more. So, suppose you are planning on training your employees, students, or others with this technology. In that case, you should ensure that the equipment you are using is compatible with the current version to avoid problems during training.
The requirement for User Education Might Become a Practice.
Learning about what to expect from this continuously changing and growing technology may require a tutorial/lesson or specialized training. As we can see how complex the Extended Reality technology is. Fortunately, most Extended Reality technology is simple enough that trainees will not have to worry about unforeseen problems. This makes staying user-friendly difficult for Extended Reality and thus it may require specialized training.
Are There Any Other Extended Realities in Development
Yes! The reality, as we know it, is experiencing a momentous shift. Today, our civilization is on the verge of a tremendous technological revolution that will propel the ‘physical realm’ we live well beyond the confines of physics and time.
Extended Reality (XR) offers access to a new realm of merging technologies defining the upcoming Metaverse. The Metaverse is an immersive, interconnected three-dimensional environment where Virtual Reality, Mixed Reality, Augmented Reality, Artificial Intelligence, Cryptocurrencies, and blockchain will alter how we exist, operate, and interact.
The potential of Extended Reality (XR) is generating expectations for a slew of previously inconceivable prospects within the rapidly growing Metaverse. By 2030, we may spend more time in the Metaverse than in the universe. People will use the Metaverse’s virtual capacities to seek employment, earn a livelihood, connect with friends, shop, and play games.
Education systems and vocational training may increasingly be given in three-dimensional virtual surroundings in the future decade. This includes boardroom and business sessions. In addition, companies and governments will depend on the Metaverse’s strength and reach to exchange data, offer services, and interact in ways never seen before.
By 2030, we expect to witness the introduction of brain-computer interfaces (BCIs), which allow the human mind to be monitored, recorded, and communicated. These Extended Reality abilities will enable us to experience experiences and past moments from someone else’s life. Meanwhile, synthetic information from simulated environments will likely drive robots to issue solutions and replace people executing tasks with more significant risks.
So, the Metaverse is one of the ongoing and upcoming Extended Reality technologies expected to soon take over the world and change the history of the Extended Reality that we already know.
FAQs
Q1. What is Extended Reality?
Extended Reality (XR) is an umbrella term that encompasses virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR). These technologies utilize complex image processing algorithms alongside immersive hardware to provide incredible experiences to individuals. Individuals utilize headsets to step into virtual worlds and can control their movements using controllers. Large tech companies such as Meta and Microsoft are working on exciting technologies. These include holograms, 3D virtual objects, haptic feedback devices and more.
Q2. What are the applications of Extended Reality?
Extended Reality is currently reshaping the way we interact, shop, work and play. It has slowly become a major part of our day to day lives. XR is being used in various industries for training and educational purposes. VR is currently taking gaming experiences to completely new levels. There are thousands of VR games readily available for users to explore. AR is being used primarily in retail where this technology enables customers to try on items before purchasing. MR is currently being utilized within the industrial sector by companies such as Heinz and Kawasaki to improve productivity and resolve supply chain issues.
Q3. Is Extended Reality important in the future?
Yes! Extended Reality includes all; virtual, mixed, and augmented reality, combining the virtual and physical worlds to create a unique world for human perceptions and interaction. This has already taken over many aspects of life, including entertainment, collaboration, training, and education. This emerging technology is becoming a massive part of our daily lives .Making it crucial for our future since everything is becoming digital. With the rise of the Metaverse, these technologies are going to become very mainstream.
Q4. What companies are working on Extended Reality?
There are hundreds of companies working on hardware and software for extended reality, these include Meta, Microsoft, NVIDIA, MojoVision, TeslaSuits, Spacewalk VR and much more. Since there are various elements involved within the creation of an immersive experience, there is plenty of room for innovation. For example, Meta and other companies are working on creating lighter and more affordable headsets. NVIDIA is working on creating its “Omniverse”, that would enable developers to create 3D virtual objects by accessing open-source libraries and much more.
Q5. What is the difference between Augmented Reality and Mixed Reality?
Both technologies perform a similar primary function, i.e., overlaying virtual objects onto physical surroundings. However, Mixed Reality offers one incredible bonus – users can interact with the virtual objects. A good example of AR is the popular game Pokémon Go. While users were able to see Pokémon through their phones, they couldn’t interact with them. In contrast, MR offers users the option to touch, move around and interact with the superimposed 3D objects, creating a very surreal experience. Thus, MR can be utilized in numerous industries such as healthcare, education, retail and much more.
References
10 Applications Of Extended Reality (XR) | Rock Paper Reality
What Is XR? 6 Examples That Demonstrate Extended Reality (makeuseof.com)
Top Extended Reality Trends In 2022 | CitrusBits
2022 Extended Reality Trends: What’s Ahead in VR/AR Application (edstutia.com)
XR System: Capabilities, Pros, And Cons – eLearning Industry
Extended Reality for Training: Pros and Cons (holopundits.com)
The Metaverse and Extended Reality | Pactera Edge
Science & Tech Spotlight: Extended Reality Technologies | U.S. GAO
The Future of Extended Reality – TFOT (thefutureofthings.com)
The 3 Types of Virtual Reality – Heizenrader
What’s the Difference Between AR, VR, and MR? | The Franklin Institute (fi.edu)
What is the Difference Between AR vs. VR and MR? | Voler Systems
XR, AR, VR, MR: What’s the Difference in Reality? – Arm Blueprint
VR, AR, MR: What are the differences between VR and AR, and MR? | Elara (elarasystems.com)
The future of the Metaverse and Extended Reality – KPMG Global (home.kpmg)
Extended Reality (XR): How It’s Changing Work and Employment – ReadWrite
What Is Virtual Reality And How Does It Work (softwaretestinghelp.com)
How does Mixed Reality Work? An Introduction to Mixed Reality – XR Today
What is augmented reality (AR), and how does it work? – News – Blippar.
If you found this article to be informative, you can explore more current Digital Twin news here exclusives, interviews, and podcasts.